The globin is recycled into amino acids which in turn are. Hemoglobin synthesis requires the coordinated production of heme and globin.

Heme Degradation Pathway Heme From Hemoglobin And Cellular Hemo Download Scientific Diagram
The process begins in the mitochondrion with the condensation of succinyl-CoA and glycine to form 5-aminolevulinic acid.
. Pages 2 Ratings 93 29 27 out of 29 people found this document helpful. Hemoglobin degradation by Plasmodium is a massive catabolic process within the parasite food vacuole that is important for the organisms survival in its host erythrocyte. Bilirubin is the end product of heme metabolism.
It is a tetrameric protein and contains the heme prosthetic group attached to each subunit. When the RBC end its life after 120 days the hemoglobin molecule is degraded. A genetic disorder it is caused by production of an abnormal type of hemoglobin called hemoglobin S which delivers less oxygen to tissues and causes erythrocytes to assume a sickle or crescent shape especially at low oxygen concentrations Figure 1835.
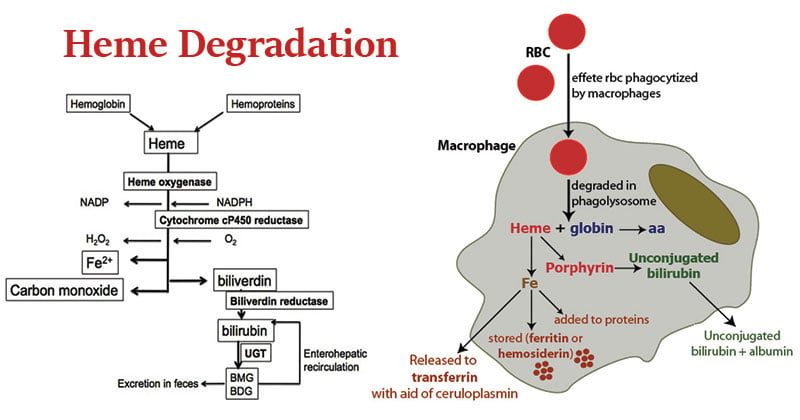
It is established that hemoglobin is transported from the host erythrocyte to the parasite digestive vacuole DV but this biological process is not well characterized. The heme initially breaks apart into biliverdin a green pigment which is rapidly reduced to bilirubin an orange-yellow pigment see bottom graphic. RBCs are engulfed by cells of the reticuloendothelial system.
The amino acids from the globin and iron are recycled while the porphyrin is degraded. These abnormally shaped cells can then become lodged in narrow capillaries because they are unable to fold in. If it is needed it is carried by Transferrin to Red Bone Marrow for incorporation into new red blood cells.
A series of steps in the cytoplasm produce. Hemolysis occurs normally in a small percentage of red blood cells as a means of removing aged cells from the blood stream and freeing heme for iron recycling. A proteolytic pathway is responsible for generating amino acids from hemoglobin.
Fate of globin The globin may be reutilized as such for the formation of hemoglobin or degraded to the individual amino acids. As the red blood cells disintegrate the hemoglobin is degraded or broken into globin the protein part iron conserved for latter use and heme see middle graphic. School Central New Mexico Community College.
These changes may be undesirable such as changes during use or desirable as in biodegradation or deliberately lowering the molecular weight of a polymer. Degradation is often due to a change in the chemical andor physical structure of the polymer chain which in turn leads to a decrease in the molecular weight of the polymer. Describe the process of hemoglobin degradationbilirubin metabolism Bilirubin is.
Four gene deletions result in Hemoglobin Barts disease Hb Barts which is incompatible with life. The other 20 comes from premature erythrocytes in the bone. In conditions like sickle cell anemia hemoglobin can have an abnormal shape.
Red blood cells which form one of the major constituents of. The absence of alpha-globin subunits allows gamma-globin subunits in utero to combine and form gamma tetramers. Overview of the Heme Degradation Pathway Degradation begins inside macrophages of the spleen which remove old and damaged senescent erythrocytes from the.
Each of the enzymes involved has its own peculiarities to be exploited for development of antimalarial agents that will starve the. Hemolysis also spelled haemolysis also called hematolysis breakdown or destruction of red blood cells so that the contained oxygen-carrying pigment hemoglobin is freed into the surrounding medium. Erythrocytes are taken up degraded by the macrophages of the reticuloendothelial RE system in the spleen liver.
Course Title PATHO 2711. Bilirubin is transferred to the bile released into the intestine and converted by bacteria to a yellow pigment. Hemoglobin is converted to a yellow pigment bilirubin the iron is stored and protein is broken down to amino acids.
Breakdown of heme to bilirubin occurs in macrophages if the reticulo-endothelial system tissue macrophages spleen liver 2. Haemoglobin is a type of globular protein present in red blood cells RBCs which transports oxygen in our body through blood. The Breakdown of red blood Cells Erythrocyte.
Solutions for problems in chapter 5. Heme the small-molecule component of hemoglobin critical for oxygen transport must undergo a complex process of metabolism and degradation described here. The major source of heme is hemoglobin found in RBCs.
Red blood cells which contain hemoglobin and other chemicals constantly undergo hemolysis and are destroyed primarily by the spleen liver and lymph nodes states Union County College. The confidence in the results is increased by the fact that they were obtained using live erythrocytes with minimum sample manipulation and therefore few artifacts. Conjugated bilirubin is then actively secreted into the bile and then the intestine.
It is a respiratory pigment and helps in transporting oxygen as oxyhaemoglobin from the lungs to different parts of the body. Bilirubin is taken up into the liver and conjugated with glucuronic acids. Iron FE3 is carried by Transferrin to the liver where it is kept as Ferritin.
Is yellow water insoluble and highly toxic. Describe the process of hemoglobin. Recycling Hemoglobin Big Picture Globin a protein is recycled to amino acids for reuse.
Unconjugated bilirubin is transported through the blood held by albumin to the liver. A late phase of heme breakdown accounting for 80 of bilirubin is from senescent red blood cells. Outline the steps in the degradation of hemoglobin to bilirubin urobilinogen and finally urobilin.
Bilirubin is the result of heme breakdown. Problems with hemoglobin can cause symptoms like fatigue and rapid heart rate. A proteolytic pathway.
Rather our data show a monotonic increase of hemoglobin degradation with the parasite development cycle and a significant difference between schizont and the ring stages. Heme is the prosthetic group that mediates reversible binding of oxygen by hemoglobin. Roughly 80 of heme destined for degradation and excretion comes from Senescent erythrocytes which have circulated for on average 3 months.
Process of Hemoglobin Breakdown In the Liver Globins and Heme Groups Inside Kupffer cells the hemoglobin is split into globins and heme groups Globins are hydrolyzed into the blood Iron is taken out of heme groups and in the process leaves bile pigment behind Kupffer Cell When. Hemoglobin breakdown pertains to the process of degrading hemoglobin into its individual components. Hemoglobin degradation by Plasmodium is a massive catabolic process within the parasite food vacuole that is important for the organisms survival in its host erythrocyte.
Urinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 16LO. Hemoglobin levels that are too high or too low can lead to health problems. An early phase of heme breakdown accounting for 20 of bilirubin is from hemoproteins heme-containing enzymes and occurs within 3 days of labeling with radioactive heme.
HbH is an unstable form of hemoglobin that precipitates and causes damage to erythrocytes as they age. Hemoglobin degradation during the asexual cycle of Plasmodium falciparum is an obligate process for parasite development and survival. About 6 g of hemoglobin per day is broken down resynthesized in an adult man 70 kg.
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from your lungs to your tissues.

Heme Degradation Pathway Heme From Hemoglobin And Cellular Hemo Download Scientific Diagram

Heme Degradation Pathway The Turnover Of Hemoglobin And Other Download Scientific Diagram

Metabolic Pathway Of The Degradation Of Heme And The Formation Of Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments